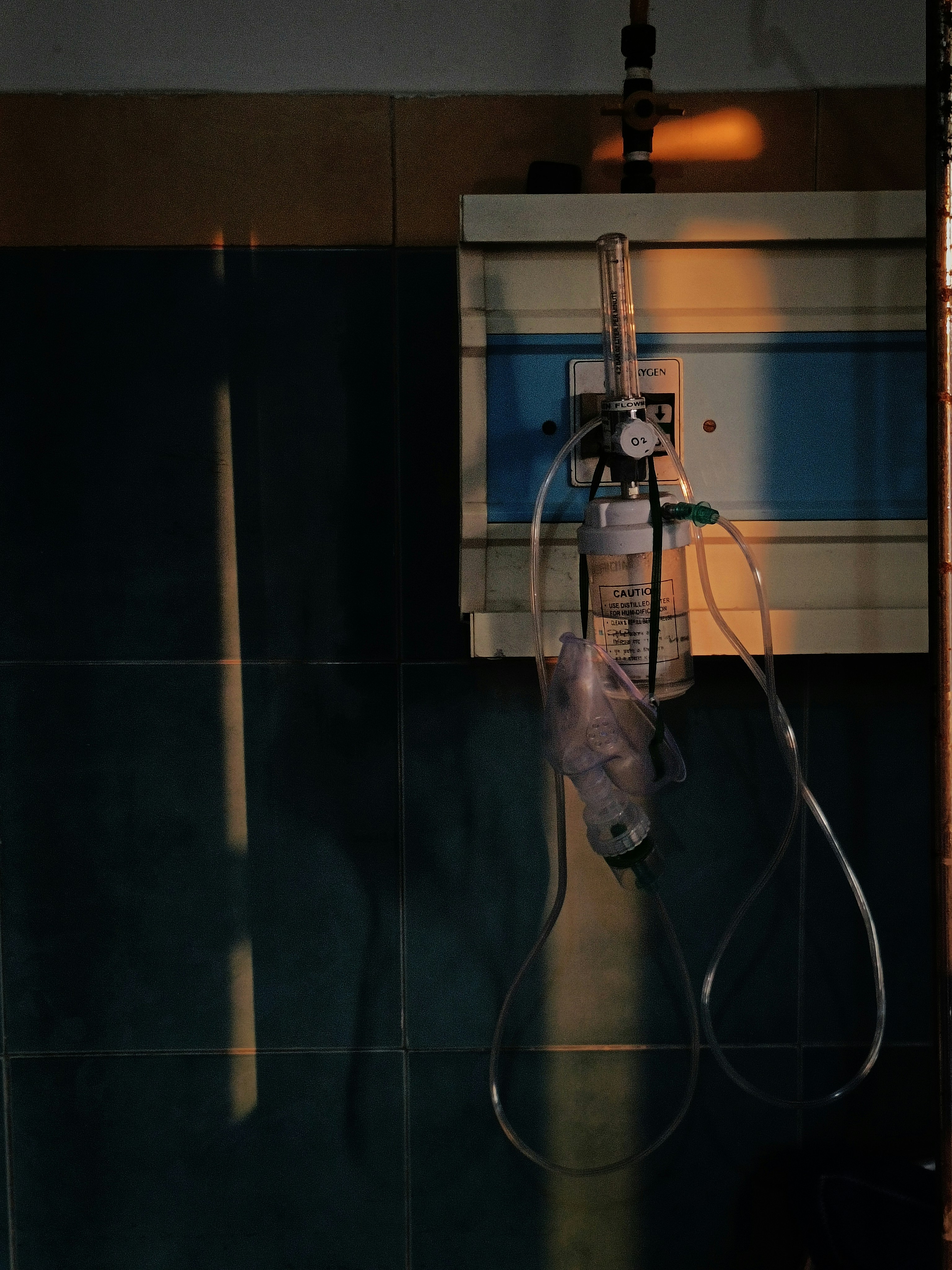Understanding Oxygen Concentrators: A Lifeline for Respiratory Illnesses
What is an Oxygen Concentrator?
An oxygen concentrator is a medical device specifically designed to provide supplemental oxygen to individuals suffering from respiratory conditions. This essential apparatus operates by taking in ambient air, filtering out nitrogen, and concentrating the oxygen it contains. The resulting oxygen-enriched air is then delivered to the patient through a nasal cannula or mask, enabling an increased supply of oxygen for inhalation. This process is particularly important for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and other respiratory disorders, where the oxygen absorption capability is diminished.
Oxygen concentrators enhance the quality of life for patients by ensuring a consistent and reliable supply of oxygen, which is often vital for their overall health and well-being. Unlike traditional oxygen tanks, which require constant refilling and transportation, concentrators are generally powered by electricity and can operate continuously or intermittently, depending on patient needs. This makes them considerably more convenient for home use or while traveling.
Moreover, modern oxygen concentrators are equipped with advanced features, such as adjustable flow settings and indicators for battery life, providing users with flexibility and ease of monitoring. Some devices even have built-in alarms that alert users in case of any operational issues, further enhancing safety.
Ultimately, the use of an oxygen concentrator plays a crucial role in assisting individuals with respiratory illnesses. By delivering a higher concentration of oxygen, the device helps improve oxygen saturation levels in the bloodstream, subsequently alleviating symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and other health complications related to inadequate oxygen supply. Thus, understanding the function and benefits of an oxygen concentrator is essential for patients and caregivers alike.
Common Illnesses That Require Oxygen Concentrators
Oxygen concentrators serve as essential medical devices for patients suffering from various respiratory illnesses. These devices provide supplementary oxygen, which is crucial for maintaining adequate oxygen levels in the blood. Several medical conditions necessitate the use of oxygen concentrators to enhance the quality of life and support respiratory function.
One of the most prevalent illnesses requiring oxygen therapy is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). This progressive condition results in airflow obstruction and difficulty breathing, making oxygen supplementation crucial for managing symptoms and preventing exacerbations. Patients with COPD often experience chronic bronchitis or emphysema, both of which can significantly impair lung function.
Pneumonia, an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, can also lead to severe respiratory complications. In more serious cases, patients may need additional oxygen to facilitate recovery and enhancement of oxygen saturation levels. Similarly, asthma, characterized by reactive airway disease, can exacerbate in severe cases, leading to the need for supplementary oxygen to alleviate respiratory distress.
Congestive heart failure, a condition where the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, can lead to fluid buildup in the lungs, thereby reducing oxygen levels. For these patients, oxygen concentrators become a vital tool for ensuring sufficient oxygenation and enhancing overall well-being. Pulmonary fibrosis, a progressive lung disease, scars lung tissue, making it difficult to breathe and necessitating oxygen therapy for comfort and functionality.
Additionally, sleep apnea, a disorder characterized by interruptions in breathing during sleep, often requires oxygen supplementation for those with severe cases. The recent COVID-19 pandemic also highlighted the importance of oxygen concentrators, as hospitalization and oxygen therapy became crucial for patients experiencing severe respiratory symptoms. Other respiratory infections further exemplify the need for oxygen support to aid recovery. Each of these conditions demonstrates the critical role oxygen concentrators play in managing respiratory health and improving patient outcomes.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) refers to a group of progressive respiratory diseases that obstruct airflow in the lungs, primarily encompassing emphysema and chronic bronchitis. The primary causes of COPD include long-term exposure to irritants that damage the lungs and airways, most notably tobacco smoke, air pollution, and occupational dust and chemicals. Genetic factors also play a role, with a rare genetic condition known as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency contributing to some cases.
The symptoms of COPD often develop gradually, making early diagnosis challenging. Common manifestations include chronic coughing, increased mucus production, wheezing, and shortness of breath, particularly during physical activities. As the condition progresses, individuals may experience more severe symptoms, leading to frequent exacerbations or flare-ups, which can significantly impede their daily activities and overall quality of life.
The importance of supplemental oxygen for COPD patients cannot be overstated. While the body’s healthy lungs effectively maintain adequate oxygen levels, COPD patients struggle to do so due to impaired lung function. When oxygen levels drop below normal, individuals experience increased shortness of breath and fatigue. Supplemental oxygen becomes essential in these cases, helping to alleviate symptoms, enhance physical activity capacity, and ultimately improve the quality of life.
Oxygen concentrators serve as a reliable solution for providing supplemental oxygen to COPD patients. These devices take in ambient air, filter out nitrogen, and deliver concentrated oxygen directly to the patient. This not only helps maintain adequate oxygen saturation levels but also reduces the strain on the heart and other organs. Furthermore, the portable nature of modern oxygen concentrators enables patients to engage in daily activities without the limitations often associated with stationary oxygen therapy.
Pneumonia and Its Impact
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lungs, primarily caused by microbial infections, which may include bacterial, viral, or fungal pathogens. The onset of this illness can vary widely, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe, depending on the causative agent and the individual’s overall health. Common symptoms of pneumonia include coughing, fever, chills, difficulty breathing, and chest pain. These symptoms can significantly hinder a patient’s daily functions and can sometimes escalate to more serious conditions that require immediate medical intervention.
The causes of pneumonia are diverse. Bacterial pneumonia is often triggered by Streptococcus pneumoniae, while viral pneumonia is frequently due to influenza viruses or coronaviruses. Fungal pneumonia, although less common, can arise from organisms like Histoplasma or Coccidioides, particularly in those with compromised immune systems. The potential complications of pneumonia can be severe, leading to respiratory failure, septic shock, or even death, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions.
For patients suffering from pneumonia, the requirement for supplemental oxygen is common due to impaired gas exchange in the lungs. Oxygen therapy serves to improve oxygen saturation levels and alleviate respiratory distress, promoting overall recovery. Oxygen concentrators play a vital role in this context, as they provide a steady supply of purified oxygen, thereby enhancing the patient’s ability to breathe comfortably. Unlike traditional oxygen tanks, which can be cumbersome and finite, oxygen concentrators continuously filter and concentrate oxygen from the ambient air, ensuring a sustainable resource for patients during their recovery journey.
Utilizing oxygen concentrators can greatly assist in managing the symptoms of pneumonia, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes. By facilitating an adequate supply of oxygen, these devices support healing processes, reduce the burden on the respiratory system, and enhance the overall quality of life for those affected.
Asthma Management with Oxygen Therapy
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to difficulty in breathing. This condition can manifest in various forms of severity, ranging from mild to life-threatening. The symptoms of asthma typically include wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and coughing, particularly during the night or early morning. Identifying triggers that exacerbate these symptoms is crucial for effective asthma management. Common triggers include allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, tobacco smoke, and pollution, as well as environmental factors like weather changes and respiratory infections.
Asthma does not affect all individuals equally; some may experience frequent attacks, while others may have well-controlled symptoms. Unfortunately, acute asthma attacks can lead to severe episodes requiring immediate medical attention. During such episodes, patients may experience significant difficulty breathing, necessitating supplemental oxygen to ensure adequate oxygen saturation levels in the blood. In these critical situations, oxygen therapy becomes an essential intervention, particularly for those struggling to maintain sufficient oxygen levels.
Oxygen concentrators serve as a vital resource during acute asthma attacks. These devices extract oxygen from the surrounding air and deliver it in concentrated form, ensuring that patients receive the oxygen they need to stabilize their condition. Utilizing an oxygen concentrator can help alleviate hypoxemia, allowing for better respiratory function and reducing the risk of further complications. For individuals with asthma, having access to an oxygen concentrator can be instrumental in managing their condition effectively, demonstrating its significance as a lifeline during respiratory emergencies. Therefore, understanding how to integrate oxygen therapy into asthma management plans is crucial for improving patient outcomes and enhancing overall quality of life.
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) and Oxygen Requirements
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) is a chronic condition that significantly impacts the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. As the heart’s pumping function declines, it fails to meet the body’s oxygen demands, leading to various symptoms that can negatively affect a patient’s quality of life. Individuals with CHF often experience shortness of breath, fatigue, and fluid retention, all of which can be exacerbated by insufficient oxygen supply.
In patients with CHF, the heart may struggle to provide the necessary blood flow to different parts of the body, particularly during periods of physical exertion or stress. This inadequacy can prompt a decrease in the oxygen levels available to vital organs, further complicating the condition. Consequently, supplemental oxygen becomes essential for many patients diagnosed with CHF. By increasing the oxygen concentration in the bloodstream, supplemental oxygen can drastically improve symptoms, thereby enhancing overall well-being.
Oxygen concentrators, which are devices specifically designed to deliver concentrated oxygen directly to patients, play a pivotal role in the management of CHF. These devices extract oxygen from the ambient air and concentrate it, ensuring a steady supply for those in need. Patients utilizing oxygen concentrators typically report a marked improvement in their ability to perform daily activities without experiencing the debilitating fatigue or breathlessness that often accompanies CHF.
Furthermore, the availability of portable oxygen concentrators allows individuals with CHF to maintain a degree of mobility and independence, which is crucial for their emotional and physical health. By integrating oxygen therapy into their daily routine, patients can manage their symptoms more effectively and potentially improve their prognosis. This underscores the importance of understanding the relationship between CHF and oxygen requirements, as it can be life-changing for those affected by this condition.
Pulmonary Fibrosis Explained
Pulmonary fibrosis is a serious respiratory condition characterized by the progressive scarring of lung tissue, which ultimately impacts the ability to breathe. This thickening and stiffening of the lung tissue can result from various causes, including long-term exposure to irritants such as environmental pollutants, occupational dust, or cigarette smoke. In some cases, it may be the result of conditions such as autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis or scleroderma) or even arise following radiation therapy or certain medications. In many instances, however, the exact cause remains unknown, and this idiopathic form particularly challenges both patients and healthcare providers.
The symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis often develop gradually, beginning with shortness of breath, especially during physical exertion. Patients may also experience a persistent dry cough that may worsen over time, fatigue, and unintended weight loss. As the disease progresses, it can lead to more severe complications, severely restricting lung function and significantly impacting quality of life. The prognosis for pulmonary fibrosis varies, but the disease is generally progressive, leading to increasing respiratory difficulties over time and necessitating effective management strategies.
One essential aspect of managing pulmonary fibrosis is the use of supplemental oxygen therapy. Many patients find that their bodies struggle to get sufficient oxygen due to the compromised lung function caused by fibrosis. This is where an oxygen concentrator becomes a vital tool. By providing a steady flow of concentrated oxygen, these devices can help alleviate symptoms such as breathlessness, enhance exercise tolerance, and improve overall respiratory function. For patients with pulmonary fibrosis, oxygen concentrators serve as a crucial lifeline, facilitating better oxygenation, thereby promoting engagement in daily activities and improving overall well-being.
The Importance of Oxygen Therapy for Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a prevalent sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breaths during sleep. This condition can significantly disrupt sleep quality, leading to excessive daytime fatigue, irritability, and complications with physical health. Individuals suffering from untreated sleep apnea often experience decreased oxygen saturation levels during sleep, which can jeopardize overall well-being. Consequently, maintaining adequate oxygen levels becomes essential for those affected by this disorder.
Oxygen therapy serves as a crucial intervention for enhancing the quality of life for individuals with sleep apnea. Supplemental oxygen can help increase the availability of oxygen in the bloodstream, promoting better sleep and potentially reducing the frequency and severity of apnea episodes. As a result, individuals utilizing oxygen therapy may experience improved cognitive function, better concentration, and a diminished risk of developing cardiovascular issues associated with hypoxemia, or low blood oxygen levels.
Oxygen concentrators play a vital role in delivering this therapy effectively. These devices filter ambient air, removing nitrogen and other gases, to produce a purified stream of oxygen. Remarkably portable and user-friendly, they are tailored to cater to the specific oxygen needs of patients, offering adjustable flow rates to optimize therapy. By ensuring adequate oxygen supply during the night, oxygen concentrators help decrease sleep disturbances and foster a more restful sleep period.
Furthermore, consistent use of oxygen therapy can enhance an individual’s overall health outcomes. With improved oxygenation, individuals may find relief from fatigue and regain energy. This transformation can lead to a more active lifestyle, contributing to better physical and mental health. Therefore, recognizing the significance of oxygen therapy in managing sleep apnea is crucial for individuals seeking effective solutions to their respiratory challenges.
Oxygen Needs in COVID-19 and Other Respiratory Infections
The emergence of COVID-19 has brought to light the critical role of oxygen therapy in managing respiratory illnesses. Patients infected with the virus often experience severe respiratory symptoms, leading to a significant decrease in oxygen saturation levels. Supplemental oxygen becomes essential for maintaining adequate oxygen levels in the blood, thereby preventing further complications associated with hypoxemia. This need is not exclusive to COVID-19; other respiratory infections, such as pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), also demonstrate a similar demand for oxygen therapy.
Oxygen concentrators emerge as vital medical devices designed to support patients requiring supplemental oxygen. Unlike traditional oxygen tanks, which store compressed oxygen, oxygen concentrators extract oxygen from ambient air and deliver it in a concentrated form to the user. This functionality is particularly advantageous in a hospital setting or home care, ensuring a continuous supply of oxygen without the logistical challenges associated with tank refills. In cases of severe respiratory infections like COVID-19, timely access to oxygen can significantly impact patient outcomes, reducing the risk of hospitalizations and improving recovery rates.
Furthermore, the portability of modern oxygen concentrators allows patients to maintain mobility during treatment, which can be crucial for mental well-being. As healthcare providers face an overwhelming number of patients requiring oxygen therapy, these devices ensure that a broader population can access necessary care. The increasing recognition of oxygen concentrators’ role in respiratory illness management has led to greater availability and advancements in technology, further enhancing their efficacy. Ensuring that patients suffering from COVID-19 and other respiratory infections receive appropriate oxygen therapy is paramount in promoting healing and improving quality of life.
Recognizing the Signs: When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
Respiratory illnesses can manifest through various signs and symptoms, often indicating the necessity for supplemental oxygen therapy. It is crucial for patients and caregivers to recognize these indicators to ensure timely medical intervention. Common signs that may suggest the need for oxygen therapy include persistent shortness of breath, fatigue during daily activities, or a rapid increase in respiratory rate. These symptoms may not only reflect the severity of a respiratory condition but also underscore the importance of appropriate management.
Additionally, individuals experiencing confusion, restlessness, or a bluish tint around the lips or fingertips should seek immediate medical advice. These symptoms can indicate low blood oxygen levels, a situation that requires urgent attention. Patients with chronic lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or pulmonary fibrosis, should be especially vigilant about any changes in their breathing patterns. Regular monitoring of oxygen saturation levels with a pulse oximeter is advisable for those at risk. A reading below 90% may warrant an assessment by a healthcare provider.
It is essential for caregivers to be proactive in noticing changes in the patient’s condition. If symptoms worsen or new symptoms arise, consulting a healthcare provider can help determine whether supplemental oxygen therapy is needed. Patients should engage with their healthcare team to discuss their symptoms and treatment options thoroughly. This dialogue can provide insights into the most suitable oxygen concentrator and therapy plan tailored to the individual’s needs. Understanding when to seek medical advice equips patients and caregivers with the necessary tools to manage respiratory illnesses effectively, ensuring improved outcomes and quality of life.